Cytokinetics Announces Preclinical Data for CK-3773274 Presented at the American Heart Association’s Basic Cardiovascular Sciences Scientific Sessions
Preclinical Studies Show CK-3773274 Produces Exposure Related Effects on Cardiac Contractility in Healthy Animals and Mouse Models of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Support Therapeutic Hypothesis for Onset of Action and Reversibility in the Clinical Setting
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.,
“We are pleased to share these important findings demonstrating that CK-274 decreases cardiac contractility in a dose- and concentration-related fashion, without changes to calcium transient. We further confirmed this effect in a mouse model of HCM and observed its effect appears reversible within 24 hours after administration with CK-274,” said Brad Morgan, Ph.D., Cytokinetics’ Senior Vice President, Research and
In vitro studies demonstrated that CK-274 selectively inhibited cardiac myosin activity, as it reduced the cardiac myosin ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 1.3 µM. Additionally, in adult rat cardiomyocytes, CK-274 reduced fractional shortening (FS), a measure of cardiac contractility, without any effect on the calcium transient.
Two in vivo studies in healthy animals also demonstrated that CK-274 decreased cardiac contractility. In healthy rats, single doses of CK-274 ranging from 0.5 to 4.0 mg/kg significantly reduced FS in a dose-related fashion relative to control treatment. Similarly, in healthy dogs, single doses of CK-274 ranging from 0.75-3.0 mg/kg decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in a dose-related fashion relative to control treatment.
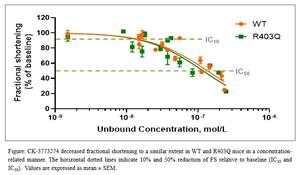
CK-274 also was evaluated in the genetic R403Q mouse model of HCM. Single doses of CK-274 ranging from 0.25-1.5 mg/kg significantly reduced FS in a dose-related fashion relative to baseline values. At all dose levels, FS returned to baseline values by 24 hours. In both the genetic R403Q mouse model of HCM and wild-type mice, CK-274 achieved a 10% reduction (IC10) in contractility at nanomolar concentrations with a >7-fold difference between the IC50 and IC10 which may translate into a measured, gradual on-target effect in patients with HCM (see Figure below).
These data indicate that CK-274 reduced cardiac contractility in vitro and in vivo and reduced fractional shortening in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner in a mouse model of HCM, suggesting that cardiac myosin inhibition may address the underlying hypercontractility of the cardiac sarcomere in hypertrophic cardiomyopathies.
About CK-274
CK-274 is a novel, oral, small molecule cardiac myosin inhibitor that company scientists discovered independent of its collaborations. CK-274 arose from an extensive chemical optimization program conducted with careful attention to therapeutic index and pharmacokinetic properties that may translate into next-in-class potential in clinical development. CK-274 was purposely designed to reduce the hypercontractility that is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). In preclinical models, CK-274 reduces myocardial contractility by binding directly to cardiac myosin at a distinct and selective allosteric binding site, thereby preventing myosin from entering a force producing state. CK-274 reduces the number of active actin-myosin cross bridges during each cardiac cycle and consequently reduces myocardial contractility. This mechanism of action may be therapeutically effective in conditions characterized by excessive hypercontractility, such as HCM.
The preclinical pharmacokinetics of CK-274 were characterized evaluated and optimized for potential rapid onset, ease of titration and rapid symptom relief in the clinical setting. The initial focus of the development program for CK-274 will include an extensive characterization of its PK/PD relationship as has been a hallmark of Cytokinetics’ industry-leading development programs in muscle pharmacology. The overall development program will assess the potential of CK‑274 to improve exercise capacity and relieve symptoms in patients with hyperdynamic ventricular contraction due to HCM.
About Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is an inherited cardiovascular disorder in which the heart muscle (myocardium) becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied). The thickening of cardiac muscle leads to the inside of the left ventricle becoming smaller and stiffer, and thus the ventricle becomes less able to relax and fill with blood. This ultimately limits the heart’s pumping function, resulting in symptoms including chest pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, or fainting during physical activity. A subset of patients with HCM are at high risk of progressive disease which can lead to atrial fibrillation, stroke and death due to arrhythmias. There are no current medical treatments that directly address the hypercontractility that underlies HCM.
About Cytokinetics
Cytokinetics is a late-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing and commercializing first-in-class muscle activators and best-in-class muscle inhibitors as potential treatments for debilitating diseases in which muscle performance is compromised and/or declining. As a leader in muscle biology and the mechanics of muscle performance, the company is developing small molecule drug candidates specifically engineered to impact muscle function and contractility. Cytokinetics is collaborating with Amgen Inc. (Amgen) to develop omecamtiv mecarbil, a novel cardiac muscle activator. Omecamtiv mecarbil is the subject of an international clinical trials program in patients with heart failure including GALACTIC-HF and METEORIC-HF. Amgen holds an exclusive worldwide license to develop and commercialize omecamtiv mecarbil with a sublicense held by Servier for commercialization in Europe and certain other countries. Cytokinetics is collaborating with Astellas Pharma Inc. (Astellas) to develop reldesemtiv, a fast skeletal muscle troponin activator (FSTA) for diseases of neuromuscular dysfunction, including SMA and ALS. Astellas holds an exclusive worldwide license to develop and commercialize reldesemtiv. Licenses held by Amgen and Astellas are subject to specified co-development and co-commercialization rights of Cytokinetics. Cytokinetics is also developing CK-274, a novel cardiac myosin inhibitor that company scientists discovered independent of its collaborations, for the potential treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathies. Cytokinetics continues its over 20-year history of pioneering innovation in muscle biology and related pharmacology focused to diseases of muscle dysfunction and conditions of muscle weakness.
For additional information about Cytokinetics, visit www.cytokinetics.com and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook and YouTube.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements for purposes of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (the “Act”). Cytokinetics disclaims any intent or obligation to update these forward-looking statements, and claims the protection of the Act's
Contact:
Cytokinetics
Diane Weiser
Vice President,
(415) 290-7757
A photo accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/19d5ef4f-6875-4c9b-a80b-c90a5ca3a427
Source: Cytokinetics, Incorporated